- Critical region: the most extreme portion of a distribution of statistical values for the null hypothesis, determined by the alpha level o If our calculated statistic falls in the most extreme position of this distribution (critical region) then we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative
- Significant Test: the p value is less than or equal to alpha in an inferential test, and the null can be rejected
o Significant because we have rejected the null hypothesis
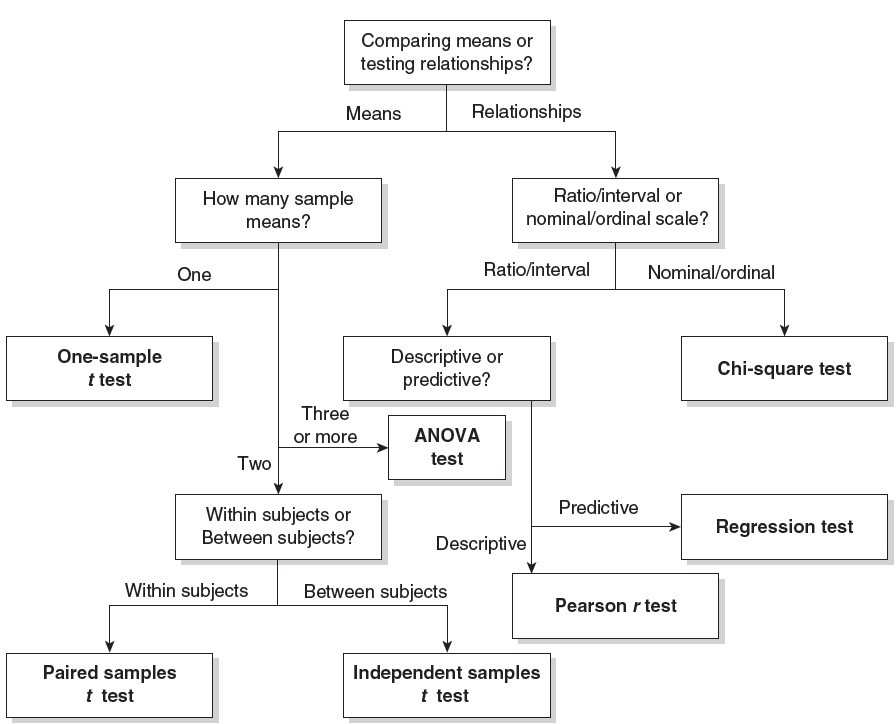
- T test: significance test used to compare means o One sample t test : used when the population mean without a treatment is known and is being compared with a sample mean that represents the population with a treatment
o Independent samples t test : used when two samples of difference individuals are compared
Each sample represents the population for that group or condition o Repeated measures t test : If two related samples or two sets of scores from the same individual are compared, this test is used
- Homogeneity of Variances: assumption of betweensubject ttests and ANOVAs that the variance in the scores in the population is equal across groups
- Main effect: test of the differences between all means for each level of an IV in an ANOVA o ANOVA tests main effects separately
- Post Hoc Tests: additional significance tests conducted to determine which means are significantly different for a main effect o Used to determine which means are different
- Interaction Effect: test the effect of one IV at each level of another IV in an ANOVA
- Sphericity Assumption: assumption of the repeated measures (within subjects) ANOVA that pairs of scores in the population have equal variance o Assumes that pairs of scores in the population have similar variability o F statistic needs to be adjusted to retain accuracy of the test
- Chi Square Test: a significance test used to determine if a relationship exists between two variables measured on nominal and ordinal scales o Used for nominal and ordinal data
- Pearson r test: significance test used to determine if a linear relationship exists between 2 variables measured on interval or ratio scales o Used for interval and ratio data
- Linear Regression : determines the best fit line to a set of data to allow prediction of the score on one variable from the score on another variable o Tests how well the data fit in a straight line